Obesity is a growing health problem that affects millions of people across the U.S. As the number of overweight Americans rises, so does the number of people who are considered severely or morbidly obese, medically classified as class III obesity formerly, which includes a BMI of 40 or higher or a BMI of 35 or more fat along with related health conditions.
Many different environmental and genetic factors can contribute to increased weight gain, from poor eating habits to high stress levels. Without the proper intervention and treatment, weight gain can escalate to dangerous levels, leading to a higher risk of diseases, health problems, significant physical disability, or even death, especially among different ethnic populations who may face unique risks associated with body fat distribution and BMI.
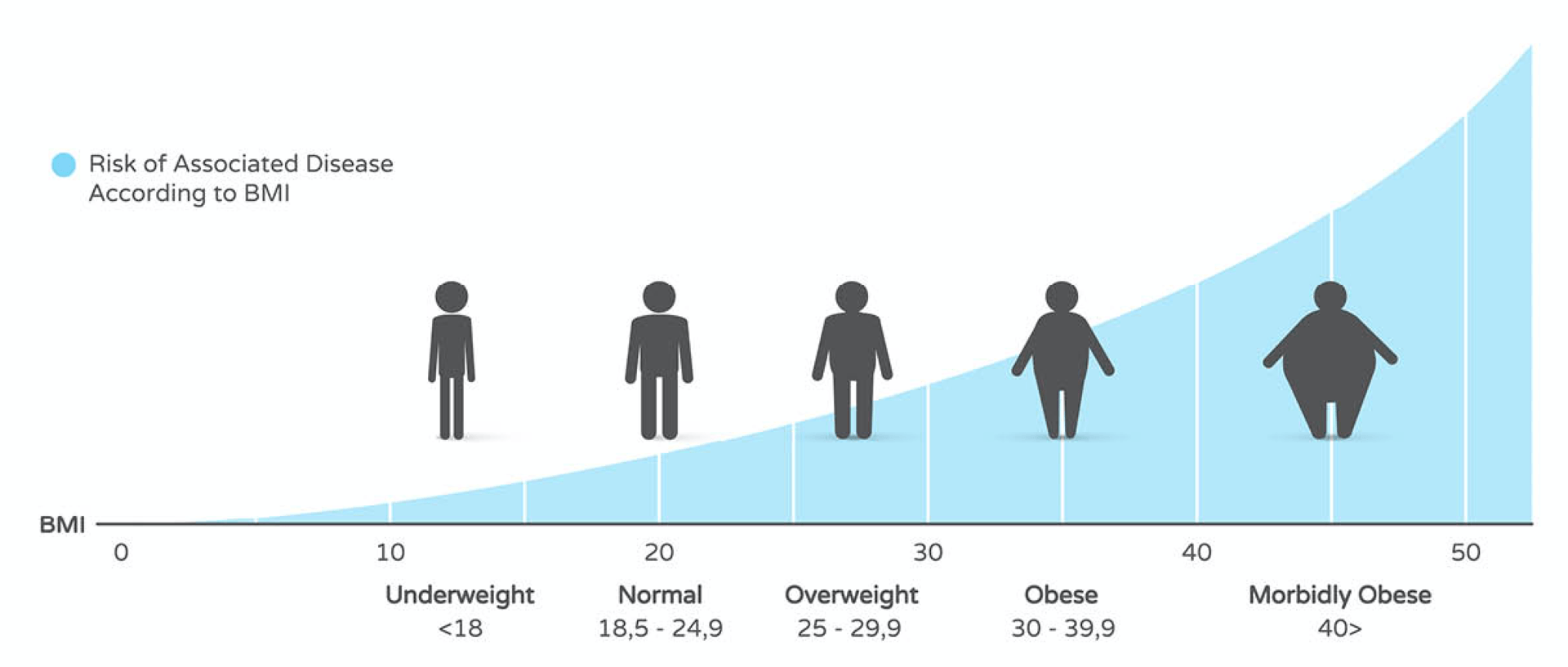
What are Morbid Obesity and Body Mass Index BMI?
Morbid obesity, formerly known as morbid, is now called class III obesity. It is a complex and progressive disease that increases the risk of developing comorbidities and weight-related health problems and interferes with the ability to perform many daily physical functions.
It is characterized as an extreme amount of excess body fat and is often measured by calculating Body Mass Index, or BMI, which is a person’s body fat based on height and weight. The World Health Organization (WHO) has proposed BMI thresholds for obesity to aid in health assessments and classifications.
A person is considered morbidly obese when they reach a body mass index of 40 or higher or are more than 100 pounds over what is considered to be an ideal body weight. Along with BMI, morbid obesity is also diagnosed when a person reaches a level of obesity that greatly increases their risk factor of developing life-threatening health problems.
Health Risks and Conditions Associated with Morbid Obesity
Morbid obesity is recognized as a chronic disease and, if left untreated, can lead to the development of one or more severe health problems. Intestinal bypass surgery has historically been used to justify insurance reimbursement for weight loss procedures in individuals classified as morbidly obese, particularly those with a BMI over 40. Central obesity, characterized by high levels of abdominal fat despite a lower waist circumference and lower overall body weight, can increase health risks, particularly in specific ethnic populations such as Asians, who may have a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes at lower BMI levels. Common conditions associated with morbid obesity include:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Heart Disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Sleep Apnea and Other Breathing Disorders
- Reproductive Problems
- Stroke
The Importance of Taking Action
Addressing morbid obesity is crucial for enhancing overall health and minimizing the risk of severe obesity-related complications. Morbid obesity, also known as class III obesity, is a serious health condition affecting millions globally. It is defined by a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher or a BMI of 35 or higher accompanied by at least one obesity-related health condition.
The significance of taking action cannot be overstated. Morbid obesity significantly increases the risk of developing critical health issues such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. It also reduces life expectancy and diminishes the quality of life. Additionally, morbid obesity can lead to conditions like obesity hypoventilation syndrome, where the lungs do not receive sufficient oxygen, and obstructive sleep apnea, where breathing is interrupted during sleep.
Addressing morbid obesity often requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Lifestyle changes include adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity. Medical interventions, such as bariatric surgery, can be highly effective. Bariatric surgery, or weight loss surgery, involves altering the stomach and intestines to reduce food intake and promote weight loss.
In addition to medical treatments, healthy lifestyle choices are essential for managing morbid obesity. This includes a healthy weight, consuming a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding unhealthy habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is also vital in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of morbid obesity.
Treatment Options for Morbid Obesity (Weight Loss Medications)
Morbid obesity is a complex medical condition, that requires a comprehensive treatment approach. The goal of treatment is to achieve a healthy body weight, improve overall health, and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications. Here are some effective treatment options:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a healthy, balanced diet low in calories and nutrients is crucial for weight loss. Working with a registered dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan that meets your needs and preferences. This plan will focus on nutrient-dense foods that promote satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is essential for burning calories and improving overall health. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be particularly beneficial. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise to help manage weight and enhance cardiovascular health.
- Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to overeating and weight gain. This therapeutic approach helps individuals develop healthier habits and coping mechanisms.
- Weight Loss Medications: In some cases, weight loss medications like orlistat and phentermine-topiramate can be prescribed to help reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness. These medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider and in conjunction with lifestyle changes to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher or those with a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions, bariatric surgery may be a viable option. Procedures such as gastric bypass surgery or sleeve gastrectomy can significantly reduce food intake and promote substantial weight loss, improving health outcomes.
Managing Morbid Obesity in Special Populations
Morbid obesity can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or ethnicity. However, certain populations may be at higher or greater risk and require tailored treatment approaches:
- Children and Adolescents: Childhood obesity is a growing concern, and morbid obesity can have severe consequences for young people. Treatment should focus on lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating and regular physical activity. Encouraging family involvement and creating a supportive environment can promote long-term healthy habits.
- Older Adults: Older adults with morbid obesity may face higher risks for age-related health conditions, such as osteoarthritis and cognitive decline. Treatment should emphasize gentle exercise, like walking or water aerobics, and a balanced diet supporting overall health while accommodating age-related dietary restrictions.
- Pregnant Women: Pregnant women with morbid obesity are at increased risk for complications such as gestational diabetes and hypertension. Treatment should focus on healthy eating and regular physical activity under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is critical for preventing and treating morbid obesity. The sooner treatment begins, the better the chances of achieving a healthy body weight and reducing the risk of obesity-related complications. Early intervention can also help prevent the development of related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
By addressing morbid obesity early, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their health and quality of life. This may involve making dietary changes, increasing physical activity, seeking behavioral therapy, or considering medical interventions like weight loss medications or bariatric surgery. Early intervention enhances the effectiveness of treatment and helps individuals build sustainable, healthy habits that can last a lifetime.
Overcoming the Challenges of Morbid Obesity
Overcoming the challenges associated with class III obesity, formerly known as morbid obesity, requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the condition. One of the most significant challenges is the stigma and discrimination that individuals with morbid obesity often face. This can make it difficult for them to seek help and support, exacerbating feelings of shame and low self-esteem.
Another challenge is the difficulty of losing weight and maintaining weight loss. Morbid obesity is a chronic condition that necessitates ongoing management and treatment. It is not merely a matter of “dieting” or an exercise program “exercising more” but a complex process involving sustainable lifestyle changes.
To overcome these challenges, seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential. This support can include working with a registered dietitian to develop a healthy eating plan, exercising with a personal trainer, and seeking counseling to address emotional and psychological issues.
Educating oneself about morbid obesity and the various treatment options available is also crucial. This includes learning about bariatric surgery, medication, and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition.
Finally, it is important to focus on progress, not perfection. Overcoming morbid obesity is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and self-compassion. It is not about achieving a “normal” weight or body shape but improving overall health and well-being.
By taking action and seeking support, individuals with morbid obesity can overcome the challenges of the condition and enhance their overall health and quality of life.
Morbid Obesity and Bariatric Surgery
For people diagnosed with morbid obesity, the risks associated with not having weight loss surgery are often higher than the risks of surgery itself. Obesity is considered a progressive disease because excess fat storage and weight gain cause several hormonal and metabolic changes in the body that increase the risk for even more significant fat accumulation over time, making it difficult to lose weight using diet and exercise alone. A multifaceted approach, including diet, exercise, and medical interventions, is often necessary to overcome the challenges associated with severe obesity.
Luckily, treatment is available, and surgery is an extremely viable option. At Birmingham Minimally Invasive Surgery, we work to educate our patients on their weight loss options, as well as life after surgery. Please schedule a consultation with us today to learn more about your weight management options and improve your health!
LEARN MORE ABOUT IF WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY IS RIGHT FOR YOU
Birmingham Minimally Invasive Surgery is a caring group of professionals specializing in all bariatric surgery types. Our surgeon, Dr. Jay Long, has highly specialized training in bariatric surgery, having completed a fellowship in minimally invasive and bariatric surgery at The Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas, where he focused on taking care of morbidly obese patients. And we are so proud of our pricing that we publish the costs right on the front page of our website! Insurance won’t pay? We offer various financing options to get the healthy body you’ve wanted for years. Visit us today at www.bmisurgery.com or call us to set up a consultation at 205-833-6907.
Conclusion
Morbid obesity is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach. By understanding the causes and consequences of morbid obesity, individuals can take the first step towards achieving a healthy body weight and reducing the risk of obesity-related complications. Treatment options, such as dietary changes, physical activity, behavioral therapy, weight loss medications, and bariatric surgery, can help individuals achieve their weight loss goals. Early intervention is critical for preventing and treating morbid obesity, and healthcare providers should work with individuals to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their unique needs.
Taking action now can significantly improve health and quality of life. If you or someone you know is struggling with morbid obesity, don’t hesitate to seek help and explore the available treatment options.

